When it comes to fabricating objects, there is a wide range of materials available to choose from that are better suited for different tasks and applications. Taking into account the desired nature, function, and performance of your product will steer you towards the best choice. Right now, plastic is a popular selection due to its versatility. Sheet metal is often the better option when deciding on materials for products due to its many advantageous characteristics. Sheet metal fabrication makes this choice possible.
What is sheet metal fabrication?
Sheet metal fabrication is a complex process of turning flat sheets of steel or aluminum into metal products via cutting, punching, folding and assembling. Metal is cut, bent or stretched into the desired shape using special tools; band saws, cutting torches, chop saws, press brakes, oxy-acetylene torches and welding equipment. The metal is then sandblasted, primed and painted.
Types of metal used in sheet metal fabrication
Sheet metal comes in a variety of types. The fabrication process adapts the metal to the chosen purpose. Common metals used in sheet metal fabrication include:
- Steel: The durability and strength of steel make it a superior choice for many uses. Low-carbon steel is used to make railings and fences. Medium carbon steel is used to fabricate parts for cars and appliances while high carbon sheet metal is found in steel wires.
- Aluminum: Aluminum is strong and lightweight. It’s good for lower temperatures so it is often used in aerospace and refrigeration. Aluminum sheet metal is used for automotive parts, electrical devices and pots/pans.
- Magnesium: The low density of magnesium makes it excellent when stiffness is required. It’s used in the transportation industry and for automotive parts.
- Brass: The acoustic properties of this lightweight, corrosion-resistant, high-strength metal make it great for a number of fittings and components.
- Bronze has a low melting point and is stronger than copper. It’s used in coins, cookware and turbines.
- Copper: The malleable nature of copper, its electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance make it perfect for conductors, electrical parts, ornaments and jewelry.
How does sheet metal fabrication work?
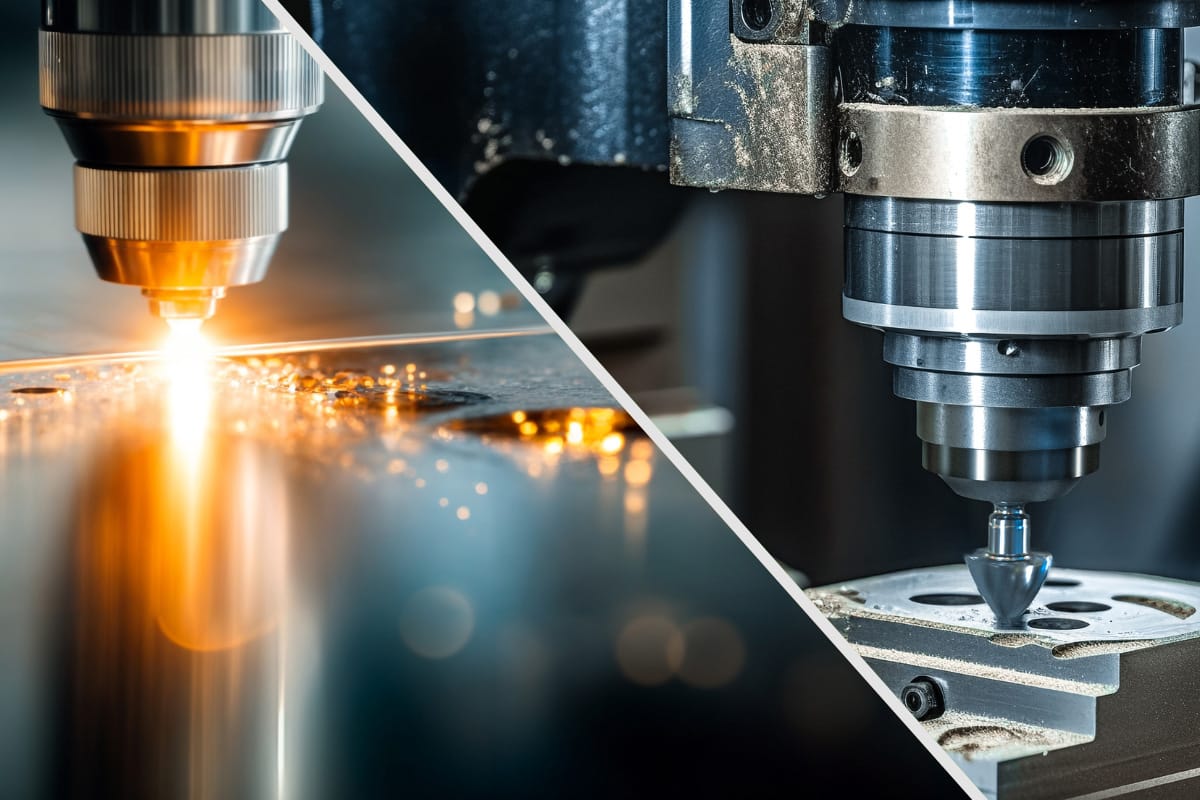
Sheet metal can be either cut or formed. The most basic sheet metal fabrication starts with a flat metal sheet and a blueprint of instructions on how to cut, form and finish the metal. The material is cut, formed, finished and joined.
1. Cutting includes the processes of shearing, cutting and blanking.
- Cutting is done with a single blade that cuts through the sheet metal.
- Blanking uses a punch to cut shaped pieces from sheet metal.
- Shearing uses an upper and lower blade (like scissors) to cut straight lines.
- Laser cutting utilizes a beam of light for cutting or engraving sheet metal, creating small detailed cuts quickly.
- Plasma cutting uses heated compressed nitrogen and hydrogen.
- Waterjet cutting utilizes concentrated streams of water filled with abrasives (garnets, aluminum oxide).
- Machining uses a drill bit or lathe blade to cut pieces of sheet metal.2.
2. Forming may involve stamping, bending, stretching and roll forming. It’s the process that reshapes the metal to the desired contours.
- Stamping used dies to press the metal into the desired form.
- Bending is done with a press or by hand, bending the metal to the desired angle.
- Stretching is achieved through the use of a hammer and dolly or English wheel.
- Roll bending creates rolls or curves using a hydraulic press, a press brake and sets of rollers.
3. Joining may involve welding, brazing, riveting and adhesives.
- Welding fuses the metal sheets together by melting them with an added filler.
- Brazing uses a torch and metal filler but does not melt the sheet metal.
- Riveting uses small metal parts to join sheet metal pieces, making it faster and less expensive than welding.
- Adhesives hold metal sheets together alone or in tandem with one of the other joining methods.
4. Finishing: Processes such as sandblasting, deburring, annealing and coating are used in the finishing operation.
Applications for sheet metal fabricating
As sheet metal fabrication is inexpensive, quick and efficient, products made from sheet metal are found everywhere! Sheet metal is used to produce brackets, cable connectors, roof flashing, rain gutters, ductwork for furnaces, MRI scanners, surgical implants, pins and plates to fix broken bones and dental instruments. Many industries utilize sheet metal fabrication; aerospace, construction, automotive, HVAC, consumer goods, robotics, agricultural, electronics and energy sectors.
Metal is a strong and lasting material and can be used in every industry. Sheet metal fabrication is easy, fast and affordable making it a great choice for many applications.
Need sheet metal fabricating services? IMS is a full-service Electronic Contract Manufacturer that offers a unique manufacturing experience with a broad scope of capabilities. Our superior customer service and commitment to excellence make us the right choice for your fabrication needs. Our knowledgeable, skilled, dedicated team of over 120 employees offers unsurpassed service and product, inspiration and innovation during the build process. Contact us for all your custom fabrication needs.