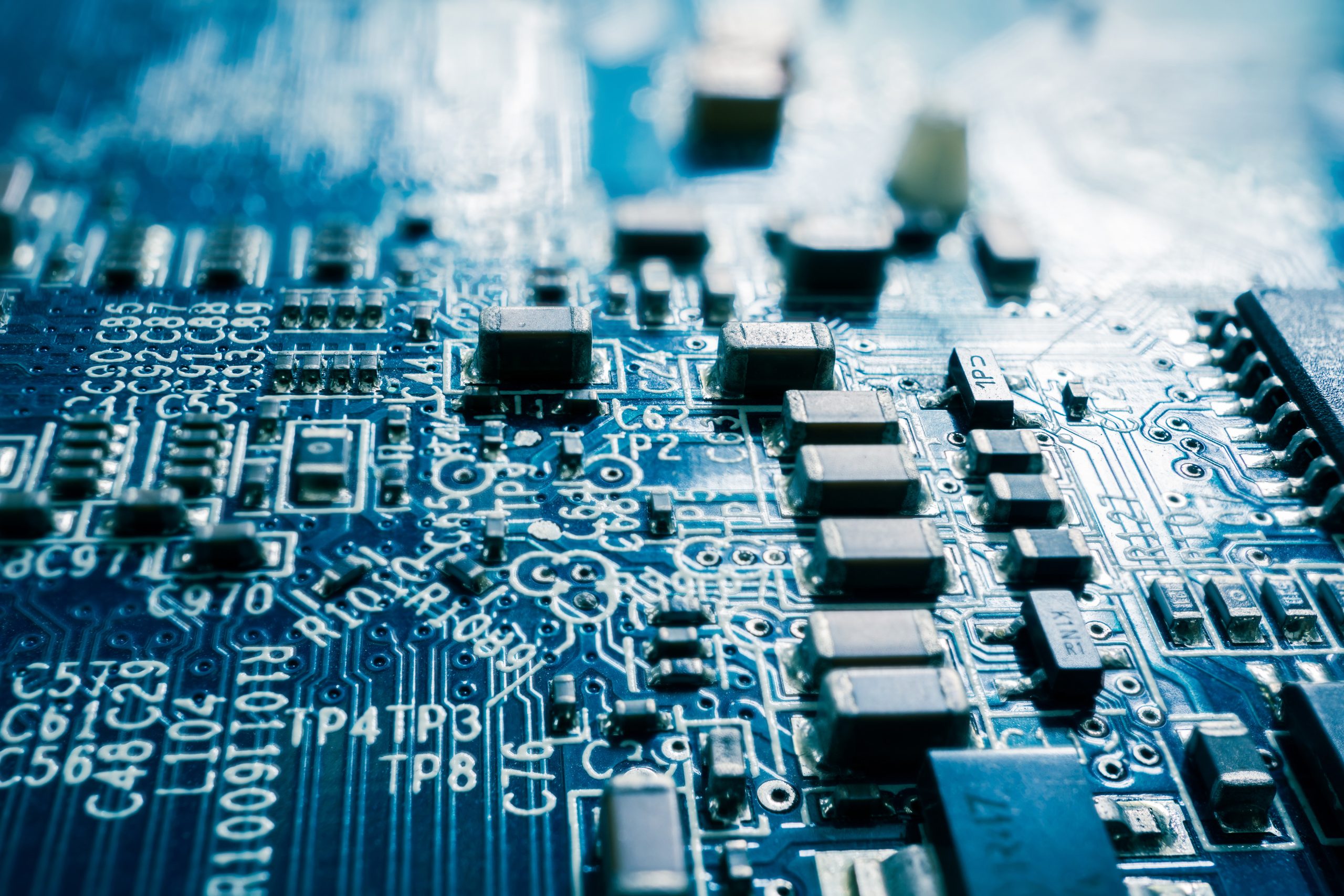
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are more than mere platforms for holding components; they are the beating heart that animates your electronic devices. From smartphones to medical devices and automotive controls, PCBs are at the heart of it all.
But what exactly are the Printed Circuit Board components, and what roles do they play? Let’s explore the anatomy of a PCB and how each component plays a crucial role in powering everything from your television to industrial equipment.
What Is a Printed Circuit Board?
A PCB is a thin, rigid board made from insulating materials like fiberglass or composite epoxy, layered with copper pathways that act as conductive routes. These copper lines are intricately designed to create a complete circuit, enabling electrical signals to flow seamlessly between components.
PCBs aren’t just where electronic parts sit; they’re designed to make sure devices work well in different fields. Whether it’s a simple circuit for a home gadget or a complex setup for things like airplanes or telecoms, PCBs turn an electrical plan into something real and usable.
They’re crucial for many devices, helping to send power and signals while ensuring everything works reliably. For these reasons, PCBs are often seen as the backbone of today’s electronics.
Printed Circuit Board Components
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is more than just a fiberglass sheet with copper tracks; it’s a central part of electronic devices, full of components that carry out specific tasks. These components all work together to make electronic systems run smoothly and efficiently.
If you’re interested in electronics or design, it helps to know what these components do. Each part on a PCB has a unique role—some manage the flow of electricity, some store energy, and others boost signals or guard the circuit against damage. The way these components are placed and connected is crucial, as it affects how well the device performs and how reliable it is.
Let’s take a look at some of the common Printed Circuit Board components and what they do:
1. Resistors
Resistors are tiny but essential components on a circuit board. They control how much electrical current flows through, preventing other parts from being overloaded. There are two main types: Surface Mount Technology (SMT) resistors, typically black and white with their resistance values marked directly on top (like 10K or 100R), and Through-Hole (TH) resistors, which often use color bands to indicate resistance, tolerance, and OHMs. As TH placement is becoming less common in favor of SMT placement, color-coded bands are also gradually being phased out. Resistors help keep everything in the circuit running smoothly by reducing voltage and splitting current, making them crucial for electronic devices.
2. Capacitors
Capacitors are like short-term energy storage units. They temporarily store and release electrical energy, which helps maintain a steady power supply and protects sensitive circuit parts from sudden surges. Capacitors smooth out voltage changes and filter noise, making sure your devices run without hiccups.
3. Transistors
Transistors are key players in amplifying and switching electrical signals in nearly all modern electronics. Think of them as tiny gates that control current flow. There are different types, like NPN, PNP, and Field-Effect Transistors (FETs), each with unique functions. Whether boosting sound in audio devices or acting as switches in digital circuits, transistors are versatile and reliable components.
4. Inductors
Inductors store energy in a magnetic field when electricity flows through them. They often work with capacitors to filter out unwanted frequencies and smooth alternating current (AC) signals. Inductors play a crucial role in managing electromagnetic interference and maintaining signal integrity in electronic devices.
5. Transformers
Transformers transfer electrical energy between circuits, either increasing or decreasing voltage levels. They’re essential for regulating power and ensuring that different parts of a circuit receive the appropriate voltage. Transformers also provide isolation, protecting sensitive components from electrical faults or surges.
6. Diodes
Diodes are like one-way gates for electrical current, allowing it to flow in only one direction. They protect circuits from reverse polarity, which could cause damage. Diodes are used for converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) and ensuring a steady power supply.
7. Sensors
Sensors detect changes in the environment, such as temperature or light, and convert these changes into electrical signals. They enable devices to respond to their surroundings, making them vital for applications needing real-time data collection and analysis.
8. Silicon Controlled Rectifiers (SCRs)
SCRs are specialized switches that handle large amounts of power. Activated by a single pulse, they control power flow in circuits, making them ideal for applications like controlling motor speed or dimming lights.
9. Integrated Circuits (ICs)
Integrated Circuits (ICs) are tiny chips packed with thousands of components like transistors and resistors. They perform various functions, from basic logic tasks to advanced data processing, and are central to the operation of modern electronics like smartphones and computers.
10. Crystal Oscillators
Crystal oscillators produce precise timing signals necessary for synchronizing operations in electronic circuits. They keep everything running smoothly and ensure accurate data processing, which is crucial for devices like microprocessors and communication systems.
11. Switches
Switches control the flow of electricity, acting like manual or automated gates in a circuit. They’re used in power buttons, toggles, or push-button configurations, allowing users to turn devices on and off easily.
12. Relays
Relays are switches controlled by electrical currents, allowing circuits to be operated remotely. They manage high-voltage circuits using low-voltage signals, playing a key role in automation and control systems.
Types of PCBs and Their Applications
Printed Circuit Boards come in different shapes and forms, each designed for specific uses. There are three main types of PCBs, each with its own benefits and challenges.
Single-sided PCBs are the most basic type. They have components on one side and copper pathways on the other. Because they are simple and affordable to make, they are perfect for basic gadgets around the house.
Double-sided PCBs feature components and pathways on both sides, which allows them to handle more complex circuits. You’ll find them in things like consumer electronics, car systems, and industrial machinery, offering a good mix of performance and cost-effectiveness.
Multi-layer PCBs consist of several layers of copper and insulating material stacked together. This design supports complex and compact circuits, making them essential for advanced technology like aerospace equipment, telecommunication devices, and powerful computers, where high performance and space-saving are key.
PCB Design Considerations
Designing PCBs requires careful planning to make sure they work well and last a long time. You need to think about things like how much current it can handle, the voltage levels, and the impedance to avoid any failures or inefficiencies.
Today, designing PCBs heavily depends on using specialized software. Programs such as Altium Designer, Eagle, and KiCAD help engineers create layouts, capture schematics, and run simulations with ease. These tools allow for precise design work on complex circuits.
It’s also important to follow design rules and standards when making PCBs. These guidelines ensure that the boards are safe, work properly, and fit well within larger electronic systems.
For more insights on how to choose the right circuit board assembly partner for your project, visit our detailed guide here.
The Future of PCB Technology
Printed Circuit Boards are constantly evolving, thanks to new trends and innovations. These changes are reshaping the way PCBs are made and used, making them even more vital in our everyday electronic devices.
One exciting trend is the rise of flexible and rigid-flex PCBs. Imagine a circuit board that can bend and twist without breaking! Flexible PCBs are perfect for things like wearables, medical gadgets, and compact electronics where space is tight. On the other hand, rigid-flex PCBs mix the best of both worlds—rigid and flexible—offering durability and lightweight designs fit for tough environments.
New materials are also playing a big role in the evolution of PCBs. Advanced plastics and composite materials are being used to boost the performance and sustainability of PCBs. This means better heat management, enhanced electrical flow, and greater resistance to things like moisture and heat. Conductive inks, made from silver or carbon, are paving the way for creative designs, especially in areas like flexible screens and smart packaging. They also help in making the manufacturing process more eco-friendly by cutting down waste and energy use.
Speaking of sustainability, the focus is shifting towards greener solutions. The industry is looking at recyclable and biodegradable materials and adopting cleaner processes. New methods like additive printing and laser etching are catching on because they reduce waste and are more precise.
Emerging tech like IoT, 5G, and automation are also shaping how PCBs are designed. Today’s devices need to be smarter and faster, which means PCBs must handle higher frequencies and complex circuits. High-density interconnect (HDI) PCBs are becoming more common because they offer more circuitry in a smaller space—a must for modern gadgets.
The future of PCBs is all about innovation, flexibility, and sustainability. With ongoing advancements, these boards are set to become more efficient, reliable, and ready to support the next wave of electronic devices.
Your Partner for Reliable, High-Quality PCB Solutions
The world of Printed Circuit Boards might sound complex, but is a fascinating and integral part of the electronics industry. Understanding the anatomy of PCBs and the functions of their components is essential for electronics engineers, designers, and enthusiasts looking to create innovative and reliable products.
At IMS, we love to push the boundaries of what is possible. If you’re eager to explore the potential of PCBs further, we have numerous resources and tools available in our Learning Hub. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or a curious tech enthusiast, the world of PCBs offers endless opportunities for discovery and innovation.
If you’re looking for precise PCB solutions, IMS offers more than 20 years of expertise, cutting-edge technology, and a relentless commitment to quality. With our collaborative, customer-first approach, we help you achieve faster time-to-market, scalability, and the reliability your customers expect. Contact us today to learn how we can support your next project.